Universal Music Group: A Music Industry Giant
- Jagannath Kshtriya
- Sep 12, 2024
- 5 min read
Universal Music Group (UMG) stands as a dominant force in the ever-evolving music industry, representing some of the most iconic artists in the world.
UMG’s best-selling artists include global superstars such as J Balvin, Justin Bieber, Luke Bryan, Lewis Capaldi, J. Cole, Daddy Yankee, Drake, Billie Eilish, Eminem, Selena Gomez, Ariana Grande, Imagine Dragons, Lady Gaga, Kendrick Lamar, Lang Lang, Lil Baby, Post Malone, Shawn Mendes, Nicki Minaj, Katy Perry, Olivia Rodrigo, Sam Smith, Chris Stapleton, Taylor Swift, Shania Twain, Morgan Wallen, and The Weeknd.
Section 1: History
Universal Music Group (UMG) has a long history closely tied to the evolution of the music industry. Starting in the early 1930s as part of Decca Records, UMG grew through strategic mergers and acquisitions, becoming a major player in the global music market, especially after joining MCA Inc. in 1962.
The 1990s brought challenges as digital technology began to disrupt the traditional music distribution model, which had relied on physical formats like CDs and vinyl. The rise of Napster in 1999, with its free file-sharing service, drastically reduced album sales and shook the industry. However, UMG quickly adapted by embracing digital distribution. It was one of the first major labels to partner with Apple’s iTunes in 2003, marking a shift from physical album sales to digital downloads.
The real turning point came with the rise of streaming platforms like Spotify in the late 2000s. UMG recognized the potential of streaming early on and invested heavily in partnerships with these services. This strategy paid off, and by the mid-2010s, streaming had become the primary revenue source for the industry, helping UMG regain its dominance.
UMG has also played a key role in preserving and monetizing music catalogs, acquiring the rights to iconic artists like The Beatles, Bob Dylan, and Taylor Swift. These catalogs have become valuable assets in the streaming era, providing steady revenue as listeners continue to enjoy both classic hits and new releases.
Today, UMG is the largest music company in the world, far surpassing its competitors in market share. Its ability to adapt to technological changes and focus on acquiring valuable music catalogs has solidified its leadership in the industry.
Since 2011, UMG has been led by Sir Lucian Grainge, who serves as Chairman and CEO.
Section 2: Business Model
UMG's business model has shifted from selling physical albums to focusing on streaming revenue. Platforms like Spotify and Apple Music are now the main sources of income, with their subscription and ad-supported models providing a steady revenue stream instead of relying on one-time album sales.
A key part of UMG's strategy is its vast music catalog. By owning the rights to a wide range of timeless songs, UMG can consistently earn money through streaming and licensing, ensuring a stable revenue base in an unpredictable industry.
UMG has ~12,000 full-time employees.
Section 3: Market Size and Opportunity
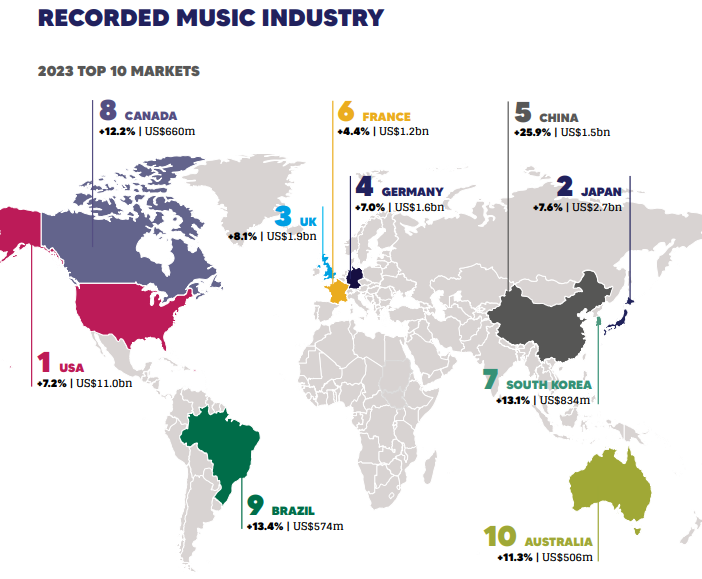
The global music streaming market has grown rapidly, especially in places like the U.S., U.K., and Sweden. In 2023, it was valued at about $34.5 billion and is expected to reach $97.5 billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of around 16% from 2024 to 2030. There is still a lot of potential in emerging markets where streaming isn't as common. UMG is in a strong position to take advantage of this global expansion.
Additionally, people are listening to more music than ever before, thanks to the widespread use of streaming services and smart devices. This rise in music consumption offers UMG more opportunities to make money from its vast music catalog and new releases.
Section 4: Competition
The "Big Three" in the music industry are the top three music companies worldwide:
Universal Music Group (UMG) (~30% of the global market): The biggest of the three, leading in recorded music, publishing, and merchandising, with a wide range of artists.
Sony Music Entertainment (~20% of the global market): A major company with many labels, strong in both recorded music and publishing.
Warner Music Group (WMG) (~15% of the global market): The third largest, with a global presence and a diverse lineup of artists, strong in recorded music and publishing.
Other competitors include independent labels like Beggars Group and XL Recordings, as well as digital streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube. These platforms are both partners and rivals, competing in areas such as artist relationships, exclusive content, and licensing deals. Publishing companies like Kobalt Music Group and BMG Rights Management also compete for control over song rights and royalties.
Section 5: Revenue and Strategy
UMG's revenue (€11 billion estimated in FY24) comes from many sources, with streaming being the largest contributor, making up over 50% of its income. Physical sales, especially vinyl records, have also made a comeback, followed by digital downloads and licensing deals.
The revenue breakdown for UMG as of 2024 is as follows:
Recorded Music: The biggest portion, making up about 76% of UMG’s revenue. This includes streaming (over 50% of total revenue), physical sales, downloads, and licensing.
Music Publishing: Contributes around 18%, including licensing, synchronization, and royalties.
Merchandising and Other: Accounts for about 6%, covering direct sales and tour merchandise.
North America made up 51% of UMG's recorded music revenue. Europe contributed 28%, Asia 13%, and Latin America and other regions each added 4%. UMG's success isn't dependent on just a few artists, as the top 50 artists together only brought in 24% of the recorded music revenue.
UMG is investing heavily in acquiring music catalogs, which are valuable long-term assets that are expected to grow in worth as streaming and digital consumption continue to rise. The company also uses advanced data analytics to improve its marketing, optimize revenue, and better understand consumer behavior, further strengthening its market position.
Section 6: Fundraising
Universal Music Group (UMG) went public on September 21, 2021, with a starting price of €18.50 per share. It is listed on the Euronext Amsterdam stock exchange under the ticker symbol "UMG."
UMG has increased its spending on acquiring music catalogs, now investing over a billion dollars annually, compared to much lower costs a few years ago. This surge is based on the belief that music rights will keep increasing in value. Strong external interest, like the partnership between Hipgnosis and Blackstone, shows widespread confidence in the long-term value of music assets, further driving UMG's expansion.
Section 7: Ownership
As of 2024, Universal Music Group's (UMG) top owners include:
Tencent Holdings Ltd.: 20%
Vivendi SE: 10%
Pershing Square Holdings: 10%
Note:
Tencent owns WeChat (a messaging and social media app) and QQ (instant messaging), and has stakes in gaming companies like Riot Games (League of Legends), Epic Games (Fortnite), and Activision Blizzard.
Vivendi owns Canal+ Group (French TV), Dailymotion (video sharing), and has interests in mobile gaming, advertising, and live entertainment.
Pershing Square is a hedge fund that invests in 8-12 companies at a time, including stakes in Restaurant Brands International, Chipotle Mexican Grill, and Howard Hughes Corporation.
Section 8: Competitive Advantage
UMG's competitive edge comes from its large scale, which enhances its ability to collect and analyze data, helping it predict trends and optimize operations. This, combined with its vast roster of top artists, attracts new talent and reinforces its industry leadership. UMG also stays ahead by quickly adapting to new technologies, like streaming, NFTs, and blockchain, ensuring it remains at the forefront of the music industry.





Comments